The nativism-empiricism debate haunts the fields of language acquisition and evolution on more than just one level. How much of children’s social and cognitive abilities have to be present at birth, what is acquired through experience, and therefore malleable? Classically, this debate resolves around the poverty of stimulus. How much does a child have to take for granted in her environment, how much can she learn from the input?
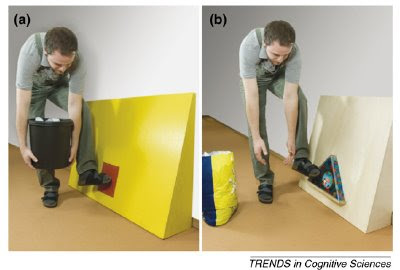
Research into imitation has its own version of the poverty of stimulus, the correspondence problem. The correspondence problem can be summed up as follows: when you are imitating someone, you need to know which parts of your body map onto the body of the person you’re trying to imitate. If they wiggle their finger, you can establish correspondence by noticing that your hand looks similar to theirs, and that you can do the same movement with it, too. But this is much trickier with parts of your body that are out of your sight. If you want to imitate someone sticking their tongue out, you first have to realise that you have a tongue, too, and how you can move it in such a way that it matches your partner’s movements.
Continue reading “Sticking the tongue out: Early imitation in infants”