Bloggingheads.tv hosts an interesting conversation between experimental philosopher Joshua Knobe and psychologist/linguist Lera Boroditsky (you should know who she is by now). It’s mostly going over the work of Boroditsky, although I thought Knobe did a good job of asking the right questions and taking a back seat when needed:
Author: James Winters
Some Links #19: The Reality of a Universal Language Faculty?
I noticed it’s almost been a month since I last posted some links. What this means is that many of the links I planned on posting are terribly out of date and these last few days I haven’t really had the time to keep abreast of the latest developments in the blogosphere (new course + presentation at Edinburgh + current cold = a lethargic Wintz). I’m hoping next week will be a bit nicer to me.
The reality of a universal language faculty? Melodye offers up a thorough post on the whole Universal Grammar hypothesis, mostly drawing from the BBS issue dedicated Evans & Levinson (2009)’s paper on the myth of language universals, and why it is a weak position to take. Key paragraph:
When we get to language, then, it need not be surprising that many human languages have evolved similar means of efficiently communicating information. From an evolutionary perspective, this would simply suggest that various languages have, over time, ‘converged’ on many of the same solutions. This is made even more plausible by the fact that every competent human speaker, regardless of language spoken, shares roughly the same physical and cognitive machinery, which dictates a shared set of drives, instincts, and sensory faculties, and a certain range of temperaments, response-patterns, learning facilities and so on. In large part, we also share fairly similar environments — indeed, the languages that linguists have found hardest to document are typically those of societies at the farthest remove from our own (take the Piraha as a case in point).
My own position on the matter is fairly straightforward enough: I don’t think the UG perspective is useful. One attempt by Pinker and Bloom (1990) argued that this language module, in all its apparent complexity, could not have arisen by any other means than via natural selection – as did the eye and many other complex biological systems. Whilst I agree with the sentiment that natural selection, and more broadly, evolution, is a vital tool in discerning the origins of language, I think Pinker & Bloom initially overlooked the significance of cultural evolutionary and developmental processes. If anything, I think the debate surrounding UG has held back the field in some instances, even if some of the more intellectually vibrant research emerged as a product of arguing against its existence. This is not to say I don’t think our capacity for language has been honed via natural selection. It was probably a very powerful pressure in shaping the evolutionary trajectory of our cognitive capacities. What you won’t find, however, is a strongly constrained language acquisition device dedicated to the processing of arbitrary, domain-specific linguistic properties, such as X-bar theory and case marking.
Babel’s Dawn Turns Four. In the two and half years I’ve been reading Babel’s Dawn it has served as a port for informative articles, some fascinating ideas and, lest we forget, some great writing on the evolution of language. Edmund Blair Bolles highlights the blog’s fourth anniversary by referring to another, very important, birthday:
This blog’s fourth anniversary has rolled around. More notably, the 20th anniversary of Steven Pinker and Paul Bloom‘s famous paper, “Natural Language and Natural Selection,” seems to be upon us. Like it or quarrel with it, Pinker-Bloom broke the dam that had barricaded serious inquiry since 1866 when the Paris Linguistic Society banned all papers on language’s beginnings. The Journal of Evolutionary Psychology is marking the Pinker-Bloom anniversary by devoting its December issue to the evolution of language. The introductory editorial, by Thomas Scott-Phillips, summarizes language origins in terms of interest to the evolutionary psychologist, making the editorial a handy guide to the differences between evolutionary psychology and evolutionary linguistics.
Hopefully I’ll have a post on Pinker and Bloom’s original paper, and how the field has developed over these last twenty years, at some point in the next couple of weeks. I think it’s historical importance will, to echo Bolles, be its value in opening up the field: with the questions of language origins and evolution turning into something worthy of serious intellectual investigation.
Other Links
Hypnosis reaches the parts brain scans and neurosurgery cannot.
Are Humans Still Evolving? (Part Two is here).
On Language — Learning Language in Chunks.
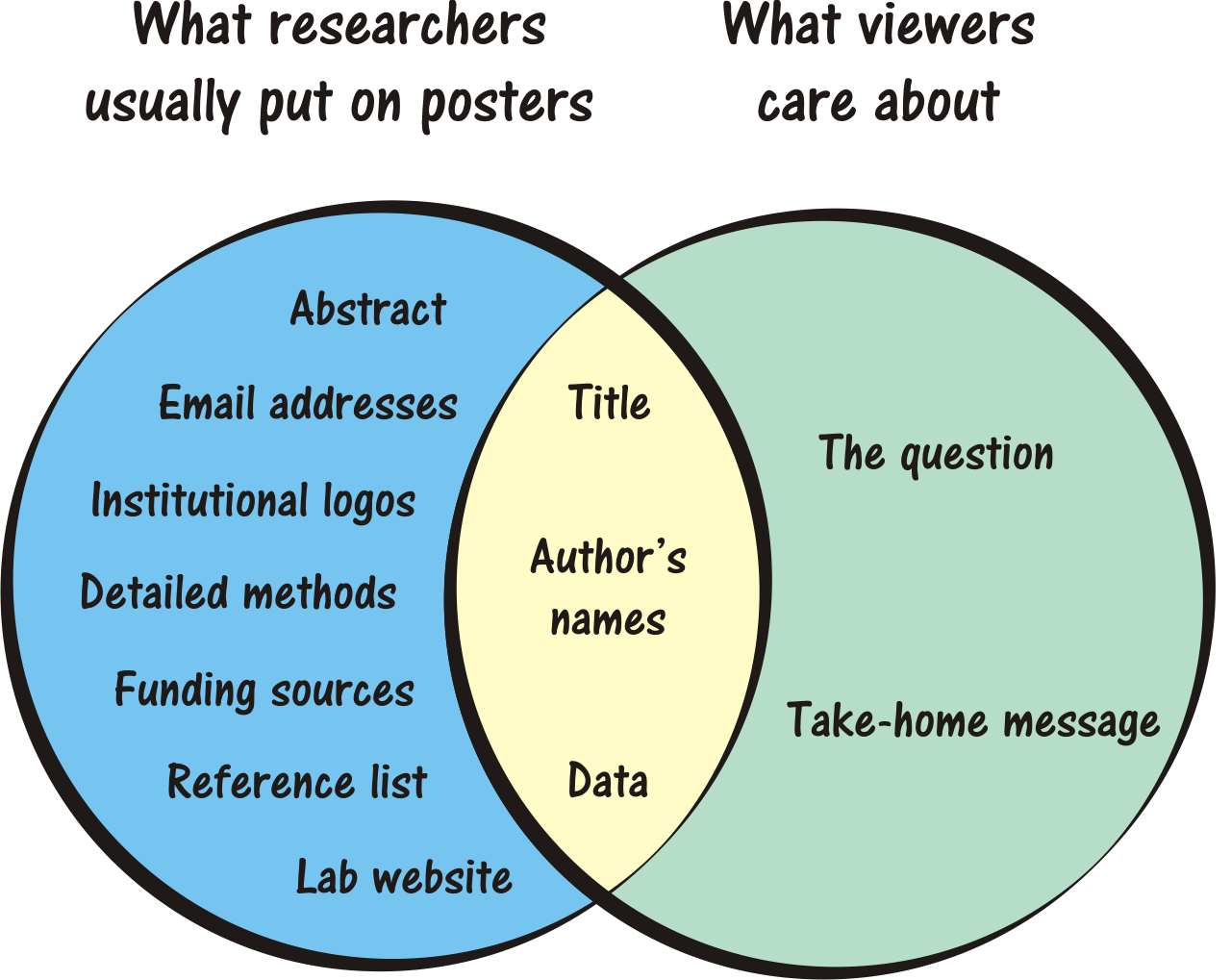
Poster Venn Diagram
Last week I presented an academic poster over at Edinburgh. Even though I’d argue it was reasonably successful, getting lots of good feedback and some useful recommendations, I still think it could have benefited from being trimmed down to highlight the main points. I’ve uploaded it to Scribd so you can see for yourself:
Phoneme Demography Poster
Since presenting I’ve come across this insanely useful poster Venn Diagram (H/T: John Hawks):
Now try and spot which aspects I didn’t cater for in my poster (hint: direct your eyes toward the right).
That’s Linguistics (Not logistics)
Linguists really need a catchy tune to match those in logistics. Any takers?
I always remember when one of my former lecturers said he was surprised by how little the average person will know about linguistics. For me, this was best exemplified when, upon enquiring about my degree, my friend paused for a brief moment and said: “Linguistics. That’s like logistics, right?” Indeed. Not really being in the mood to bash my friend’s ignorance into a bloody pulp of understanding, I decided to take a swig of my beer and simply replied: “No, not really. But it doesn’t matter.” Feeling guilty for not gathering the entire congregation of party-goers, sitting them down and proceeding to explain the fundamentals of linguistics, I have instead decided to write a series of 101 posts.
With that said, a good place to start is by providing some dictionary definitions highlighting the difference between linguistics and logistics:
Linguistics /lɪŋˈgwɪs.tɪks/ noun
the systematic study of the structure and development of language in general or of particular languages.
Logistics /ləˈdʒɪs.tɪks/ plural noun
the careful organization of a complicated activity so that it happens in a successful and effective way.
Arguably, linguistics is a logistical solution for successfully, and rigorously, studying language through the scientific method, but to avoid further confusion this is the last time you’ll see logistics in these posts. So, as you can probably infer, linguistics is a fairly broad term that, for all intensive purposes, simply means it’s a discipline for studying language. Those who partake in the study of language are known as linguists. This leads me to another point of contention: a linguist isn’t synonymous with a polyglot. Although there are plenty of linguists who do speak more than one language, many of them are quite content just sticking to their native language. It is, after all, possible for linguists to study many aspects of a language without necessarily having anything like native-level competency. In fact, other than occasionally shouting pourquoi when (drunkly) reflecting on my life choices, or ach-y-fi when a Brussels sprout somehow manages to make its way near my plate, I’m mainly monolingual.
Matt Ridley’s contractual silence
This morning I just received my copy of Matt Ridley’s latest book, The Rational Optimist: How prosperity evolves. I must admit that, despite being a big fan of Ridley’s writings, I found myself somewhat disillusioned since his role in the subprime mortgage crisis at Northern Rock. In particular, I was always confused as to why Ridley never defended himself against scathing attacks from the likes of George Monbiot. Maybe it was an admission of guilt? Perhaps. But I now have a somewhat more satisfying explanation for the silence:
I am writing in times of unprecedented economic pessimism. The world banking system has lurched to the brink of collapse; an enormous bubble of debt has burst; world trade has contracted; unemployment is rising sharply all around the world as output falls. The immediate future looks bleak indeed, and some governments are planning further enormous public debt expansions that could hurt the next generation’s ability to prosper. To my intense regret I played a part in one phase of this disaster as non-executive chairman of Northern Rock, one of many banks that ran short of liquidity during the crisis. This is not a book about that experience (under terms of my employment there I am not at liberty to write about it). [my emphasis].
So there you have it: a contractual obligation to keep schtum. It’s a shame, really, as I would hate to be in a position where I am not even given the opportunity to defend my position, especially on a topic that generated a massive amount of news and speculation.
As for the book: so far, so good. It’s also a lot larger than I expected. I do have some minor quibbles, but they can wait until I write a more thorough review.
Some quick announcements
Just thought I’d make three quick announcements:
First, I decided to drag myself into the age of 140-characters and (albeit begrudgingly) joined Twitter. I say begrudgingly because my day is already packed with plenty of distractions besides adding Twitter into the mix… But I noticed it’s the place where all the cool science bloggers are gathering, and gradually coagulating into an amorphous cloud of science networking, so I thought I might as well sign up (ever the follower, never the trendsetter).
Second, if you happen to find yourself in Edinburgh on Friday October 1st, then you can come and see me and Sean presenting our respective posters (click here and here for the abstracts) at the 24th Language at Edinburgh Lunch. I’m sure, for me at least, it’ll be quite a sobering experience in highlighting how little I know about phonology, phonetics, sociolinguistics and demography. On the plus side I’ll get some free food 🙂 .
Lastly, if you happened to click on my poster abstract, then the more observant of you will have noticed I’m now affiliated with Cardiff University. Yes, that’s right, I’m doing yet another masters course. This time it’s at the Centre for Language and Communication Research, with the idea being that I’ll get a more solid foundation in research methodology etc before pursuing a PhD or research assistant position.
That is all.
Genetic Anchoring, Tone and Stable Characteristics of Language
In 2007, Dan Dediu and Bob Ladd published a paper claiming there was a non-spurious link between the non-derived alleles of ASPM and Microcephalin and tonal languages. The key idea emerging from this research is one where certain alleles may bias language acquisition or processing, subsequently shaping the development of a language within a population of learners. Therefore, investigating potential correlations between genetic markers and typological features may open up new avenues of thinking in linguistics, particularly in our understanding of the complex levels at which genetic and cognitive biases operate. Specifically, Dediu & Ladd refer to three necessary components underlying the proposed genetic influence on linguistic tone:
[…] from interindividual genetic differences to differences in brain structure and function, from these differences in brain structure and function to interindividual differences in language-related capacities, and, finally, to typological differences between languages.”
That the genetic makeup of a population can indirectly influence the trajectory of language change differs from previous hypotheses into genetics and linguistics. First, it is distinct from attempts to correlate genetic features of populations with language families (e.g. Cavalli-Sforza et al., 1994). And second, it differs from Pinker and Bloom’s (1990) assertions of genetic underpinnings leading to a language-specific cognitive module. Furthermore, the authors do not argue that languages act as a selective pressure on ASPM and Microcephalin, rather this bias is a selectively neutral byproduct. Since then, there have been numerous studies covering these alleles, with the initial claims (Evans et al., 2004) for positive selection being under dispute (Fuli Yu et al., 2007), as well as any claims for a direct relationship between dyslexia, specific language impairment, working memory, IQ, and head-size (Bates et al., 2008).
A new paper by Dediu (2010) delves further into this potential relationship between ASPM/MCPH1 and linguistic tone, by suggesting this typological feature is genetically anchored to the aforementioned alleles. Generally speaking, cultural and linguistic processes will proceed on shorter timescales when compared to genetic change; however, in tandem with other recent studies (see my post on Greenhill et al., 2010), some typological features might be more consistently stable than others. Reasons for this stability are broad and varied. For instance, word-use within a population is a good indicator of predicting rates of lexical evolution (Pagel et al., 2007). Genetic aspects, then, may also be a stabilising factor, with Dediu claiming linguistic tone is one such instance:
From a purely linguistic point of view, tone is just another aspect of language, and there is no a priori linguistic reason to expect that it would be very stable. However, if linguistic tone is indeed under genetic biasing, then it is expected that its dynamics would tend to correlate with that of the biasing genes. This, in turn, would result in tone being more resistant to ‘regular’ language change and more stable than other linguistic features.
Continue reading “Genetic Anchoring, Tone and Stable Characteristics of Language”
A history of evolution pt. 2: The Wealth of Nations, Populations and On the Origin
Some Links #18: GxExC
The depression map: genes, culture, serotonin, and a side of pathogens. Another new science blog network (Wired) and once again a new stable of good science writers. I’m particularly pleased to see that David Dobbs, a former SciBling and top science writer, has found a new home for Neuron Culture. I was also pleased to see he had written an article on studies into the interactions between genes and culture, namely: Chiao & Blizinsky (2009) and Way & Lieberman (2010). And I was even more pleased to see that he’d mentioned both mine and Sean’s posts on the social sensitivity hypothesis. Suffice to say, I was pleased.
Take home paragraph:
In a sense, these studies are looking not at gene-x-environment interactions, or GxE, but at genes x (immediate) environment x culture — GxExC. The third variable can make all the difference. Gene-by-environment studies over the last 20 years have contributed enormously to our understanding of mood and behavior. Without them we would not have studies, like these led by Chiao and Way and Kim, that suggest broader and deeper dimensions to what makes us struggle, thrive, or just act differently in different situations. GxE is clearly important. But when we leave out variations in culture, we risk profoundly misunderstanding how these genes — and the people who carry them — actually operate in the big wide world.
The same issues are not as operative when it comes to culture. Two tribes can speak different dialects or languages. If a woman moves from one tribe to another her children don’t necessarily speak a mixture of languages, rather, they may speak the language of their fathers. The nature of cultural inheritance is more flexible, and so allows for the persistence of more heritable variation at different levels of organization. Differences of religion, language, dress, and values, can be very strong between two groups who have long lived near each other and may be genetically similar.
Homo was born vocalizing. Babel’s Dawn links to a recently finished PhD thesis that supposedly argues for a relatively recent emergence for language (approx. 120,000 years ago). She defends her assertions by stating: “[…] all of the unique cognitive traits attributed to humans arose as the consequence of one crucial mutation, which radically altered the architecture of the ancestral primate brain.” I haven’t read the thesis, and I probably won’t as I’m already stretched in regards to my reading, but I’m completely unconvinced by the hopeful mutation hypothesis. Plus, as Bolles notes in his post, there is plenty of available evidence to the contrary.
Primed for Reading. Robert Boyd reviews Stanislas Dehane’s new book, Reading in the Brain: The Science and Evolution of a Human Invention, which I’ll be picking up soon. In the meantime, to give you a bit of background, I suggest you read Dehane’s (2007) paper on the Neuronal Recycling Hypothesis: the Cultural recycling of cortical maps. H/T: Gene Expression.
Through the looking glass (part 1). The Lousy Linguist reviews Guy Deutscher’s new book, Through the Language Glass: Why the World Looks Different in Other Languages, with the general takeaway message being that, in part one at least, one where the book is a bit science-lite. What really interested me, though, were these two paragraphs:
We discover quite quickly what Deutscher is doing as he begins to walk through complexity issues of “particular areas of language” (page 109), namely morphology, phonology, and subordination. And these last 15 pages are really the gem of Part 1. He shows that there is an interesting, somewhat illogical, entirely engaging but as yet unexplained set of correlations between speaker population size and linguistic complexity.
For example, languages with small numbers of speakers tend to have more morphologically rich grammars (hence one could claim that small = more complex). However, small languages with small numbers of speakers also tend to have small phonological inventories. Hmmm, weird, right? [My emphasis]
As those of you who read this blog will know: I don’t think it’s weird that small speaker populations also tend to have small phonological inventories.
Clothing lice out of Africa. A cool new paper by Troups et al which looks at the evolutionary history of clothing lice to provide specific estimates on the origin of clothing. Using a Bayesian coalescent modelling approach, they estimate that clothing lice diverged from head louse ancestors between 83,000 and 170,000 years ago. H/T: Dienekes.
Language and Complexity: Evolution Inside Out
Here is a video of Terrence Deacon, someone who needs no introduction on this website, giving a talk at Irving K. Barber Learning Centre about his latest research into language evolution:
Continue reading “Language and Complexity: Evolution Inside Out”